
Mastering the Crypto Market: Top 5 Trading Strategies for 2024
Cryptocurrency trading is a high-risk, high-reward venture that demands a well-thought-out strategy. Here we delve into five of the most effective strategies: Moving Average Crossovers, Relative Strength Index (RSI), Event-Driven Trading, Dollar Cost Averaging (DCA), and Scalping.
1. Moving Average Crossovers
A moving average (MA) is a lagging technical indicator that combines the price points of an asset over a specific period, averaged to form a single trend line. This trend line helps traders identify the direction of the trend while smoothing out random price fluctuations.
The crossover strategy involves two main types: price crossovers and moving average crossovers.
- Price Crossovers: This occurs when the asset’s price crosses above or below a moving average, indicating a potential change in trend. Traders wait for this crossover to decide when to enter or exit a position.
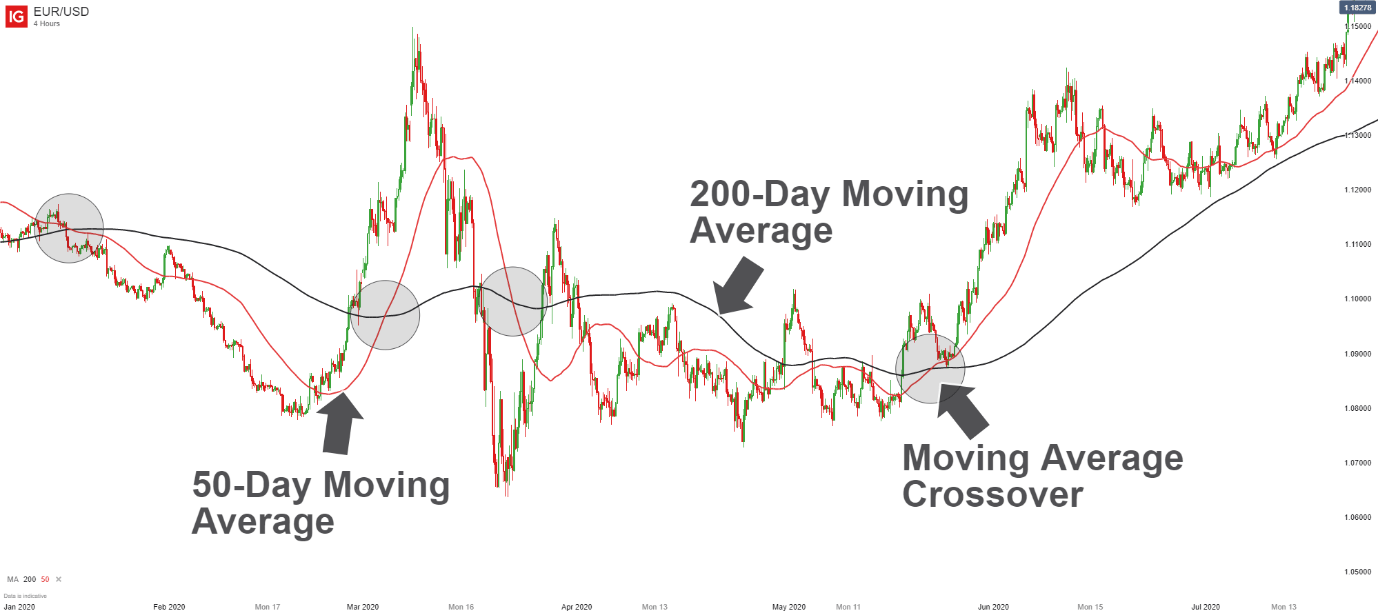
- Dual Moving Averages: This method applies two moving averages—short-term and long-term—to the price chart. When the short-term MA crosses above the long-term MA, it signals a bullish trend, known as the ‘golden cross.’ Conversely, when the short-term MA crosses below the long-term MA, it signals a bearish trend, referred to as the ‘death cross.’
Practical Example
A trader might set up a 50-day MA and a 200-day MA on a Bitcoin chart. When the 50-day MA crosses above the 200-day MA, the trader enters a long position, anticipating a bullish run. Conversely, when the 50-day MA crosses below the 200-day MA, the trader exits the position or shorts the asset.
2. Relative Strength Index (RSI)
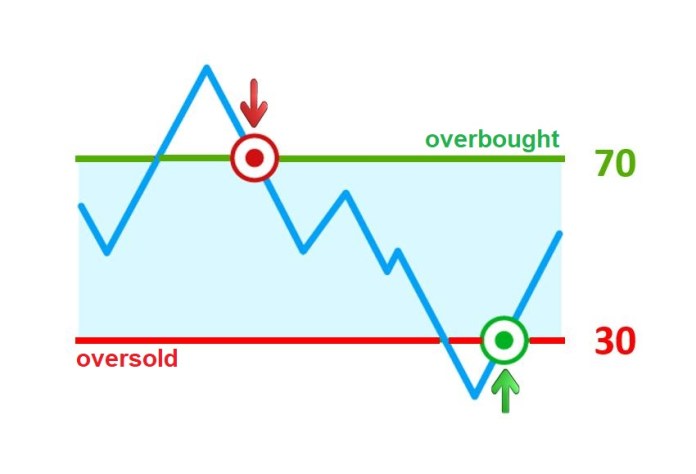
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) is a momentum oscillator that measures the speed and change of price movements. It ranges from 0 to 100 and helps identify overbought or oversold conditions of an asset.
The RSI is calculated using the formula:
RSI = 100 - (100 / (1 + RS))
where RS is the average of X periods’ up closes divided by the average of X periods’ down closes.
RSI is used to detect potential buy and sell signals. When RSI is above 70, the asset is considered overbought and might be due for a price correction. When RSI is below 30, the asset is considered oversold, potentially indicating a buying opportunity. Traders also look for divergence between RSI and price movements to predict reversals.
Practical Example
If Ethereum’s RSI drops below 30, indicating an oversold condition, a trader might buy Ethereum expecting a price rebound. Conversely, if the RSI rises above 70, the trader might sell or short Ethereum anticipating a price drop.
3. Event-Driven Trading
Event-driven trading involves making trades based on news and events that can affect the price of cryptocurrencies. This strategy leverages the market’s reaction to events such as regulatory news, technological advancements, and significant corporate announcements.
- Pre-Event Strategy: Traders often monitor for patterns of consolidation before an anticipated news release. They position themselves to capitalize on the breakout that typically follows.
- Post-Event Strategy: Due to the unpredictable nature of the crypto market, some traders prefer to act after the news has been released, allowing them to gauge the market reaction and make more informed decisions.
Practical Example
A trader might buy Bitcoin after positive regulatory news from a major country or sell Ethereum after a significant hack on its network. This strategy requires staying updated with news and having the agility to act quickly.
4. Dollar Cost Averaging (DCA)
Dollar Cost Averaging (DCA) is a strategy where an investor divides the total amount to be invested across periodic purchases of a target asset. This approach aims to reduce the impact of volatility on the overall purchase.
Instead of investing a lump sum, the investor buys smaller amounts of the asset at regular intervals, regardless of the price.
Practical Example
An investor decides to invest $1,200 in Bitcoin over a year. Instead of buying $1,200 worth of Bitcoin at once, they purchase $100 worth of Bitcoin each month. This strategy reduces the risk of buying at a peak price and allows the investor to benefit from price drops.
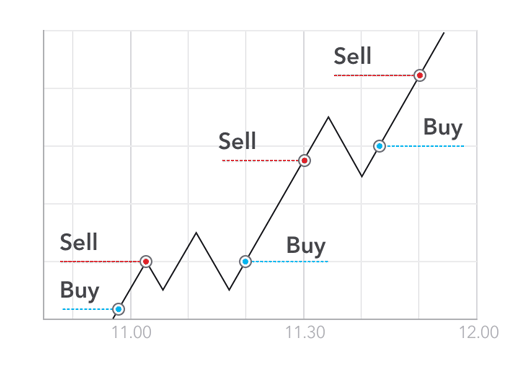
5. Scalping
Scalping is a day trading strategy that involves making numerous trades throughout the day to profit from small price movements. Scalpers aim to “scalp” small profits repeatedly.
Scalping requires a trader to have a solid understanding of the market, quick decision-making skills, and the ability to execute trades rapidly. Scalpers use various technical indicators and tools to identify short-term opportunities.
Practical Example
A scalper might identify a pattern in the minute-by-minute price movements of Litecoin. By rapidly buying and selling Litecoin, the scalper profits from small price fluctuations throughout the day.
Conclusion
These strategies provide a robust framework for navigating the volatile world of cryptocurrency trading. By understanding and applying Moving Average Crossovers, RSI, Event-Driven Trading, Dollar Cost Averaging, and Scalping, traders can better manage risks and capitalize on market opportunities.
This article is for general information purposes and is not intended to be and should not be taken as legal or investment advice. The views, thoughts, and opinions expressed here are the author’s alone and do not necessarily reflect or represent the views and opinions of AltcoinStudio.
